By Solomon Asuquo
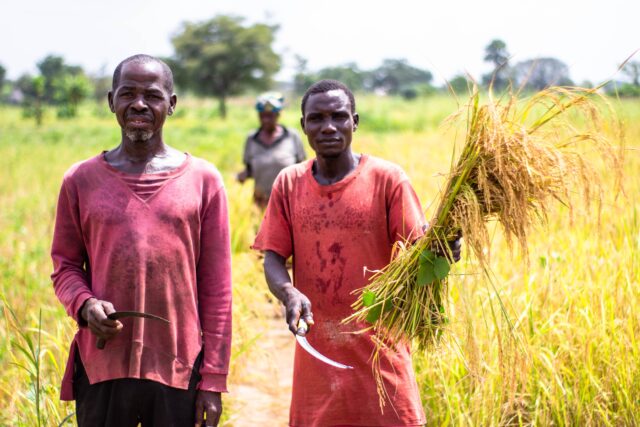
Climate change has become one of the most pressing global challenges of our time. The need for urgent action to mitigate and adapt to climate change has become increasingly apparent. While various sectors contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, in this article, I will share with you how the food system holds significant potential for climate action particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. In Nigeria for instance, with the establishment of many food processing companies, The food system encompasses all the processes and activities involved in the production, processing, distribution, and consumption of food. By adopting sustainable practices within the food system, I believe we can make substantial progress in addressing climate change and building a more resilient future.
Let’s take a look at some of the ways in which Food Action Accelerates Climate Action in Subsaharan Africa
- The Impact of Food on Climate Change:
The food system is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. It is estimated that food production and supply chains account for about one-third of global greenhouse gas emissions. This includes emissions from deforestation, land use change, agricultural practices, transportation, and food waste. The intensive use of fossil fuels, chemical fertilizers, and pesticides in agriculture further exacerbates the environmental impact on the food system. Therefore, transforming our food system is crucial for achieving climate goals.
“Transitioning to sustainable agricultural practices can play a vital role in mitigating climate change.”
2. Sustainable Agriculture and Ecosystem Restoration:
Even though the majority of the farmers in the region are subsistence, some of their activities are harmful to the planet Earth. Transitioning to sustainable agricultural practices can play a vital role in mitigating climate change. Sustainable agriculture focuses on regenerative farming techniques that promote soil health, biodiversity, and water conservation. Practices such as organic farming, agroforestry, and precision agriculture reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve soil carbon sequestration, and enhance the resilience of ecosystems. By adopting sustainable agricultural practices, we can restore degraded lands, protect biodiversity, and mitigate climate change simultaneously.
3. Reducing Food Loss and Waste:
Food loss and waste contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Approximately one-third of the food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally. This not only represents a significant waste of resources but also leads to unnecessary emissions. When food decomposes in landfills, it generates methane, a potent greenhouse gas. By implementing measures to reduce food loss and waste throughout the supply chain, we can lower emissions, conserve resources, and improve food security.
4. Shifting Towards Sustainable Diets:
The food choices we make have a direct impact on the environment. Shifting towards sustainable diets that are plant-based, low in carbon-intensive animal products, and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Livestock production, particularly the rearing of ruminant animals, is a major source of methane and nitrous oxide emissions. By promoting sustainable diets and raising awareness about the environmental impact of food choices, we can empower individuals to make more climate-friendly decisions.
5. Strengthening Food Systems Resilience:
Climate change poses risks to food systems, including increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, water scarcity, and disruptions to agricultural productivity. Building resilience within food systems is essential to adapt to these challenges. This involves enhancing agroecological practices, diversifying crops, investing in climate-smart infrastructure, and improving access to financial resources and technology for small-scale farmers. Strengthening the resilience of food systems will not only ensure food security but also enable communities to cope with climate-related shocks and stresses.
In conclusion, I will like to add that Addressing climate change requires a holistic approach that encompasses various sectors, and the food system plays a pivotal role in this endeavor. By embracing sustainable agriculture, reducing food loss and waste, promoting sustainable diets, and enhancing the resilience of food systems, we can accelerate climate action and create a more sustainable future. Governments, businesses, civil society organizations, and individuals all have a role to play in transforming the food system and realizing its potential as a powerful lever for climate mitigation and adaptation. It is through collective action and collaboration that we can build a resilient and climate-smart food system that nourishes both people and the planet.